What’s the Difference between Digital and Offset Printing?
Digital and Offset printing both produce high quality printed products like brochures and flyers.
But the processes they use are complete different, which means each has their pros and cons, and work better for marketers depending on their requirement.
Offset Print
Offset printing involves a large machine rolling a wet-ink design onto paper. For this, aluminium rolls (plates) must be created from scratch, one for each colour (CMYK). Offset takes a lot of time and resources to set up, but once the machine is rolling it is highly cost effective for large volume print runs.
Ideal for:
- Large print runs (1000+)
- Printing to forecast
- Storage and distribution over time.
Digital Print
Digital printing is different. Here colour is laid onto the paper one dot at a time by the machine, which is much like your printer at home or in the office (but bigger). It doesn’t take a lot of time to set up and is highly cost-effective for short print runs.
Ideal for:
- Small print runs (less than 1000).
- Printing on demand.
- Delivery as needed.
Cost v Quantity
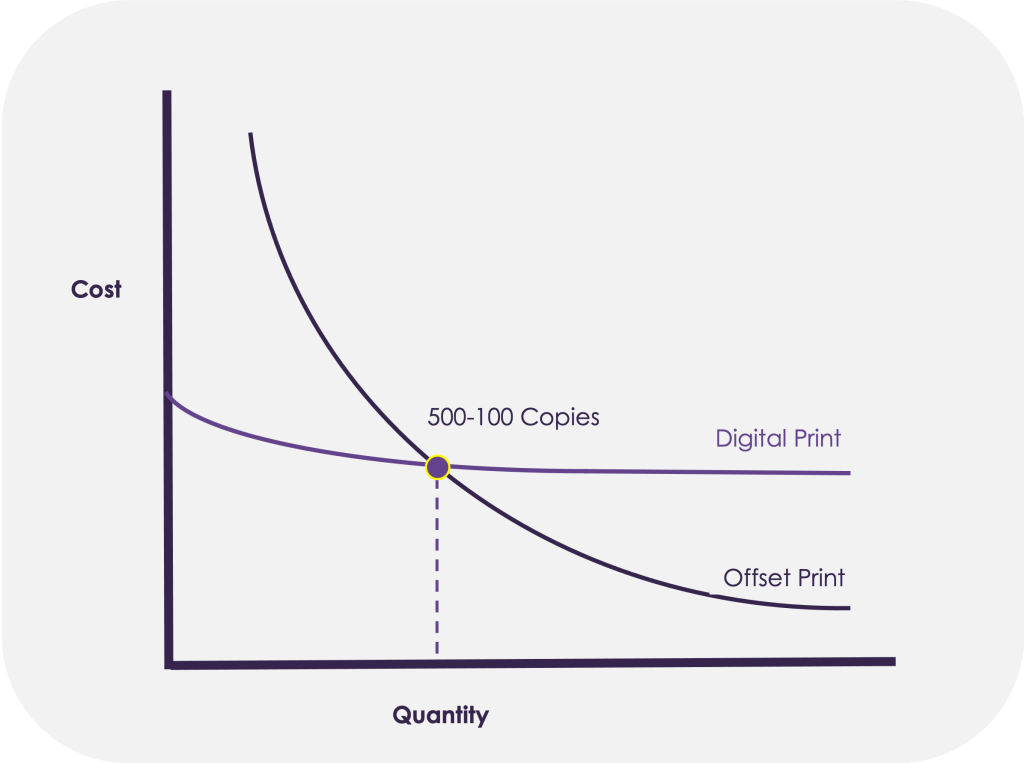
Comparing Digital with Offset Printing
Speed
Very fast. 1-3 days depending on the complexity of the printing requirement.
Slower. Generally, 4-7 days depending on the complexity of the print requirement.
Quality
Very high quality and sufficient for most marketing collateral.
The highest quality of printing, capable of printing intricate designs.
Cost Effectiveness
Cost effective at low volumes (below 1000) but relatively expensive above that.
Cost effective at high volumes and relatively expensive at lower volumes.
Types
Ideal for single A4 (2 pages) and A4 folded flyers (4 pages) and smaller brochures (8-24 pages).
Suitable for any size printing requirement.
Flexibility
Fully flexible. Files can be updated at any time, keeping collateral current when it is distributed to market.
No flexibility. Once printed the content is locked in for the life of the product.
Customisation
Doable at no extra cost. Collateral can be localised for each market (images and information can be adjusted as required).
Impossible, unless at extreme cost. One size must fit all.
Conclusion
Digital and offset print both have their advantages and disadvantages for producing marketing collateral for international student recruitment activities and events.
But for international marketers who want to reduce the environmental impact of their marketing collateral, localised digital printing offers a more sustainable way to put high quality printed collateral in the hands of their recruiters.
